http://ask.xmodulo.com/create-configure-mysql-user-command-line.html
Here is how to create and configure a MySQL user on Linux.
You first log in to MySQL server as the root.
To verify that the account is created successfully, run:
is expressed as a comma-separated
list of privileges. If you want to grant privileges for any database (or
table), place an asterisk (*) in the database (or table) name.
For example, to grant CREATE and INSERT privileges for all databases/tables:
To grant all privileges to all databases/tables:
, you can specify multiple resource limits separated by space.
For example, to add MAX_QUERIES_PER_HOUR and MAX_CONNECTIONS_PER_HOUR resource limits:
The last important step after creating and configuring a MySQL user is to run:
Question: I would like to create a new user
account on MySQL server, and apply appropriate permissions and resource
limits to the account. How can I create and configure a MySQL user
from the command line?
To access a MySQL server, you need to log in to the server using a
user account. Each MySQL user account has a number of attributes
associated with it, such as user name, password, as well as privileges
and resource limits. Privileges are user-specific permissions defining
what you can do inside a MySQL server, while resource limits set the
limitations on the amount of server resource allowed for for the user.
Creating or updating a MySQL user involves managing all these attributes
of the user account.Here is how to create and configure a MySQL user on Linux.
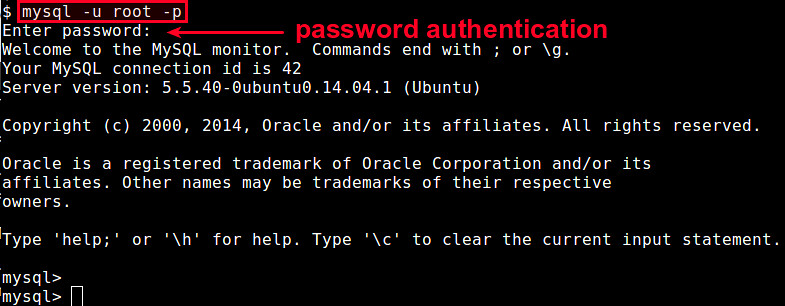
You first log in to MySQL server as the root.
$ mysql -u root -p
When prompted for authentication, enter the MySQL root password.
Create a MySQL User
To create a new user with username 'myuser' and password 'mypassword', use the following command.
mysql> CREATE USER 'myuser'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'mypassword';
Once a user is created, all its account details including an
encrypted password, privileges and resource limits are stored in a table
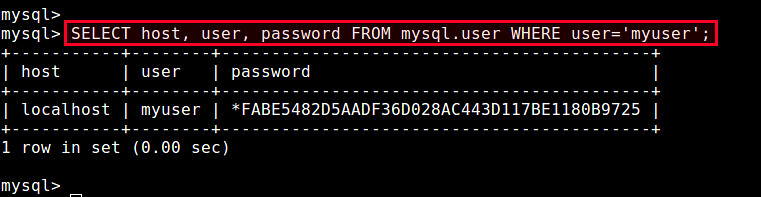
called user in a special database named mysql.To verify that the account is created successfully, run:
mysql> SELECT host, user, password FROM mysql.user WHERE user='myuser';

Grant Privileges to MySQL User
A newly created MySQL user comes with zero access privilege, which means that you cannot do anything inside MySQL server. You need to grant necessary privileges to the user. Some of available privileges are the following.- ALL: all privileges available.
- CREATE: create databases, tables or indices.
- LOCK_TABLES: lock databases.
- ALTER: alter tables.
- DELETE: delete tables.
- INSERT: insert tables or columns.
- SELECT: select tables or columns.
- CREATE_VIEW: create views.
- SHOW_DATABASES: show databases.
- DROP: drop daabases, tables or views.
mysql> GRANT ON . TO 'myuser'@'localhost';
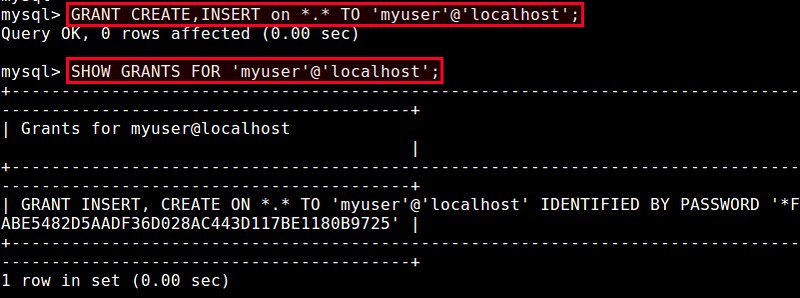
In the above, For example, to grant CREATE and INSERT privileges for all databases/tables:
mysql> GRANT CREATE, INSERT ON *.* TO 'myuser'@'localhost';
To verify the granted privileges of the user:
mysql> SHOW GRANTS FOR 'myuser'@'localhost';

To grant all privileges to all databases/tables:
mysql> GRANT ALL ON *.* TO 'myuser'@'localhost';
You can also remove existing privileges from a user. To revoke
existing privileges from the account 'myuser', use the following
command.
mysql> REVOKE ON . FROM 'myuser'@'localhost';
Add Resource Limits to MySQL User
In MySQL, you can place limits on MySQL resource usage for individual users. The available resource limits are the following.- MAX_QUERIES_PER_HOUR: number of allowed queries per hour.
- MAX_UPDATES_PER_HOUR: number of allowed updates per hour.
- MAX_CONNECTIONS_PER_HOUR: number of allowed logins per hour.
- MAX_USER_CONNECTIONS: number of simultaneous connections to the server.
mysql> GRANT USAGE ON . TO 'myuser'@'localhost' WITH
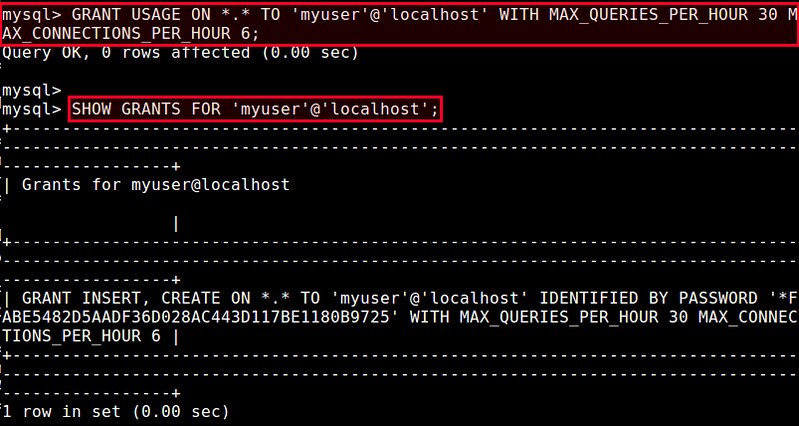
In For example, to add MAX_QUERIES_PER_HOUR and MAX_CONNECTIONS_PER_HOUR resource limits:
mysql> GRANT USAGE ON *.* TO 'myuser'@'localhost' WITH MAX_QUERIES_PER_HOUR 30 MAX_CONNECTIONS_PER_HOUR 6;
To verify the resource limits of the user:
mysql> SHOW GRANTS FOR 'myuser'@'localhost;

The last important step after creating and configuring a MySQL user is to run:
mysql> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
so that the changes take effect. Now the MySQL user account is good to go!
No comments:
Post a Comment