https://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/run-commands-on-linux-instance-at-launch-using-cloud-init
I would like to perform common automated configuration tasks and run commands/scripts after the LXD instance starts. How to use cloud-init to run commands on my Linux Container (LXD) instance at launch time?
LXD can use the cloud-init directive to run commands or scripts at the first boot cycle when you launch an instance using the lxc command.
One can create a CentOS 7 based Linux container too:
You can apply certain profile too:
First line must be #cloud-config:
Next, I want to run ‘apt-get upgrade’ on first boot to download and install all security updates for my Linux container, so append:
Setup hostname and domain name and update /etc/hosts file:
Run the following commands on first boot. In this case, update sshd to listen only on private IP and reload sshd, append:
To view your lxc config for foo container, run:
Sample outputs:
Wait for 2-5 minutes. To run all above tasks.
Verify that sshd bind to private IP:
Verify that packages are installed and system updated:
You can see the actual process logs for cloud-init's processing of the configuration file here:
Output of your commands can be found here:
I would like to perform common automated configuration tasks and run commands/scripts after the LXD instance starts. How to use cloud-init to run commands on my Linux Container (LXD) instance at launch time?
LXD can use the cloud-init directive to run commands or scripts at the first boot cycle when you launch an instance using the lxc command.
What is a cloud-init?
cloud-init handles early initialization of a cloud instance including LXD and Linux containers. By default cloud-init installed in the Ubuntu/CentOS and all other major cloud images. With cloud-init you can configure:
Sample cloud-init file for lxc/lxd
- Hostname
- Update system
- Install additional packages
- Generate ssh private keys
- Install ssh keys to a users .ssh/authorized_keys so they can log in without a password
- Configure static IP or networking
- Include users/groups
- Creating files
- Install and run chef recipes
- Setup and run puppet
- Add apt or yum repositories
- Run commands on first boot
- Disk setup
- Configure RHN subscription and more.
Step 1: Create lxc container
Type the following command to create a Ubuntu LXC container called foo (but do not run the lxc container yet):$ lxc init ubuntu: fooOne can create a CentOS 7 based Linux container too:
$ lxc init images:centos/7/amd64 barYou can apply certain profile too:
$ lxc init images:ubuntu/xenial/amd64 C2 -p staticlanwanStep 2: Create yml cloud-init config file
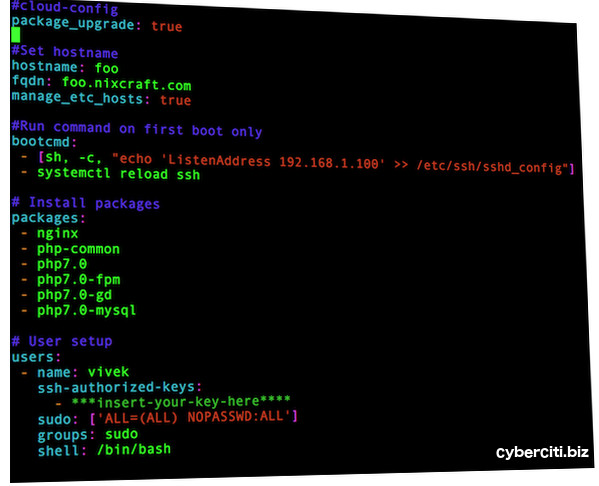
In this example, I’m going to setup my lxc hostname, update my system, and Install ssh keys to a users .ssh/authorized_keys so they can log in without a password:$ vi config.xmlFirst line must be #cloud-config:
#cloud-configNext, I want to run ‘apt-get upgrade’ on first boot to download and install all security updates for my Linux container, so append:
# Apply updates using apt
package_upgrade: trueSetup hostname and domain name and update /etc/hosts file:
# Set hostname
hostname: foo
fqdn: foo.nixcraft.com
manage_etc_hosts: trueRun the following commands on first boot. In this case, update sshd to listen only on private IP and reload sshd, append:
#Run command on first boot only bootcmd: - [sh, -c, "echo 'ListenAddress 192.168.1.100' >> /etc/ssh/sshd_config"] - systemctl reload sshYou can install php7 and nginx packages as follows, append:
# Install packages packages: - nginx - php-common - php7.0 - php7.0-cli - php7.0-common - php7.0-fpm - php7.0-gd - php7.0-mysql - php7.0-opcache - php-pearFinally, install a ssh-key for vivek login and add vivek to sudo file too, append:
# User setup
users:
- name: vivek
ssh-authorized-keys:
- ***insert-your-key-here****
sudo: ['ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD:ALL']
groups: sudo
shell: /bin/bash
Save and close the file.Step 3: Pass cloud-init directives to an instance with user data
You need to set a user.user-data variable as follows for foo Linux container:$ lxc config set foo user.user-data - < config.yml To view your lxc config for foo container, run:
$ lxc config show fooSample outputs:
name: foo
profiles:
- default
config:
user.user-data: "#cloud-config\npackage_upgrade: true\n\n#Set hostname\nhostname:
foo\nfqdn: foo.nixcraft.com\nmanage_etc_hosts: true\n\n#Run command on first boot
only\nbootcmd:\n - [sh, -c, \"echo 'ListenAddress 192.168.1.100' >> /etc/ssh/sshd_config\"]\n
- systemctl reload ssh\n \n# Install packages\npackages:\n - nginx\n - php-common\n
- php7.0\n - php7.0-fpm\n - php7.0-gd\n - php7.0-mysql\n\n# User setup\nusers:\n
- name: vivek\n ssh-authorized-keys:\n - ***insert-your-key-here****\n sudo:
['ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD:ALL']\n groups: sudo\n shell: /bin/bash\n\n"
volatile.apply_template: create
volatile.base_image: 315bedd32580c3fb79fd2003746245b9fe6a8863fc9dd990c3a2dc90f4930039
volatile.eth0.hwaddr: 00:16:3e:3d:d9:47
volatile.last_state.idmap: '[{"Isuid":true,"Isgid":false,"Hostid":100000,"Nsid":0,"Maprange":65536},{"Isuid":false,"Isgid":true,"Hostid":100000,"Nsid":0,"Maprange":65536}]'
devices:
root:
path: /
type: disk
ephemeral: false
Step 4: Start your container
Type the following command:$ lxc start fooWait for 2-5 minutes. To run all above tasks.
Step 5: Verify it
To login to foo LXC, enter:$ lxc exec foo bashVerify that sshd bind to private IP:
$ netstat -tulpnVerify that packages are installed and system updated:
$ sudo tail -f /var/log/apt/history.logA note about LXD not working with cloud-init
Please note that cloud-init in LXD triggers after network is up. In other words if network defined as DHCP or static but failed to get an IP address may result into hang ups in cloud-init. It will fail without much warning. Set the following command prior to the first container startup as described in step #4:$ lxc config set foo user.network_mode link-local
$ lxc start fooLog files for LXD
If you are having problems with cloud-init or cloud-config, take look at the following log files:$ lxc exec foo bashYou can see the actual process logs for cloud-init's processing of the configuration file here:
# tail -f /var/log/cloud-init.log Output of your commands can be found here:
# tail -f /var/log/cloud-init-output.log
No comments:
Post a Comment