https://www.fossmint.com/backup-restore-linux-with-timeshift
 Timeshift is an open-source system restore tool that creates incremental filesystem snapshots using either of 2 modes: BTRFS snapshots or rsync+hardlinks.
Timeshift is an open-source system restore tool that creates incremental filesystem snapshots using either of 2 modes: BTRFS snapshots or rsync+hardlinks.
With it, you can schedule backups at multiple levels using filters and the backups can be restored from Live CD/USB or directly from the system while it is running.
The goal of Timeshift is to maintain the history and integrity of your file system files and settings and not to back up your media files or documents. To do that, you will need a different backup app.
RSYNC Mode backups are made using rsync and hard-links
and while each snapshot is a full backup that can be browsed using a
file manager, all snapshots share common files in order to save disk
space.
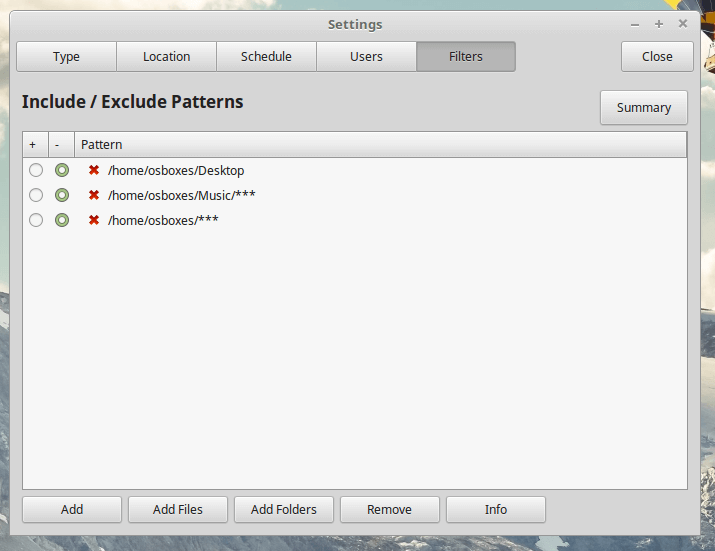
I advise that you reconfigure the app after completing the setup wizard steps so you will be able to select user directories that you want to include or use filters to specify files that you want the backup process to include or ignore.
You can always change your settings to fit a different backup scheme from the settings tab.
Within the Settings tab are 5 other tabbed sections: Type, Location, Schedule, Users and Filters.
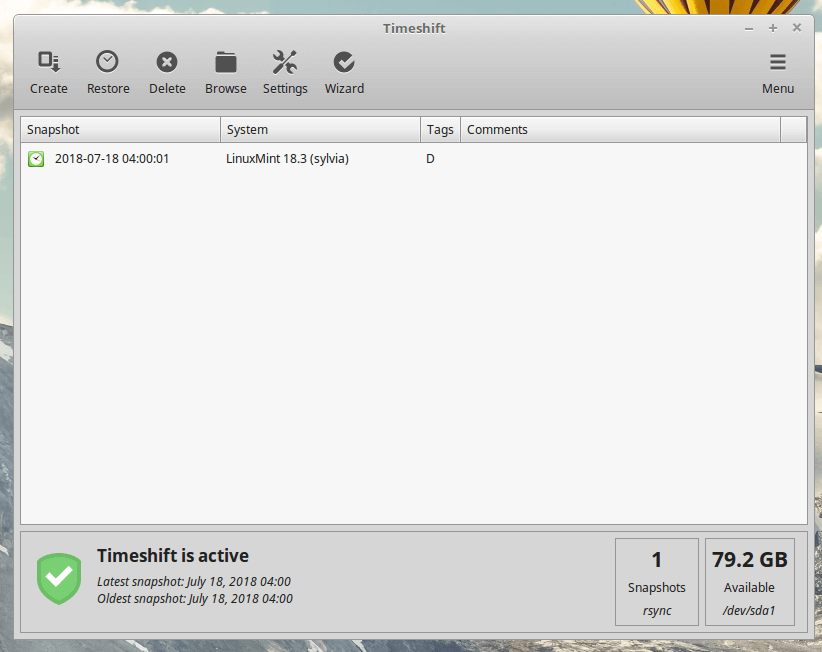
All snapshots will be listed in Timeshift’s main screen. Highlight anyone on the list and click the Restore button to revert to a previous time as saved in the snapshot.
Remember that using Timeshift, requires you to have a sufficient amount of memory to hold at least 1 snapshot. You can reduce the number of backup levels to as little as 1 by unchecking the backup levels to keep only one selected.
You can reduce the snapshots count in the Schedule tab and set the snapshot number to 5 or less. You can also disable automatic backups and create snapshots manually whenever you need one done.
As you can see, Timeshift is easy to use thanks to its helpful descriptions and hints.
How much of a Timeshift user are you? Do you use it to also backup your documents and media files or do you use it for only system snapshots and use a different backup tool for your files?
Drop your comments in the discussion section below.
 Timeshift is an open-source system restore tool that creates incremental filesystem snapshots using either of 2 modes: BTRFS snapshots or rsync+hardlinks.
Timeshift is an open-source system restore tool that creates incremental filesystem snapshots using either of 2 modes: BTRFS snapshots or rsync+hardlinks.With it, you can schedule backups at multiple levels using filters and the backups can be restored from Live CD/USB or directly from the system while it is running.
The goal of Timeshift is to maintain the history and integrity of your file system files and settings and not to back up your media files or documents. To do that, you will need a different backup app.
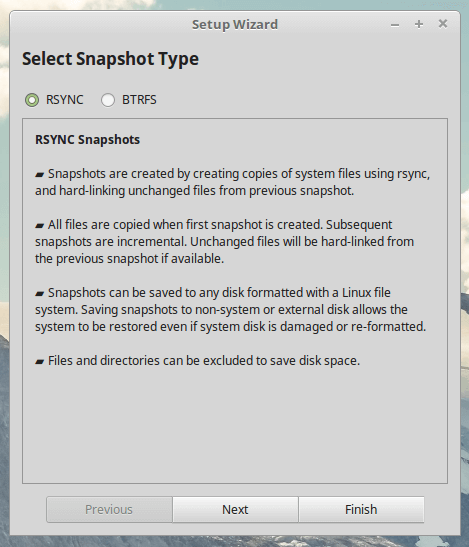
What’s the difference between BTRFS mode and RSYNC mode?
BTRFS Mode creates backups using the BTRFS filesystem’s inbuilt features and the snapshots are supported on only systems that have an Ubuntu-type subvolume layout.How to Install Timeshift in Linux
Timeshift is comes pre-installed on Linux Mint. To install it on other Linux distributions such as Ubuntu and its derivatives, enter the terminal commands below.$ sudo add-apt-repository -y ppa:teejee2008/ppa $ sudo apt-get update $ sudo apt-get install timeshiftOn Arch Linux, you can install Timeshift using yaourt command as shown.
$ sudo yaourt timeshiftOn other Linux distributions such as Fedora, CentOS and RHEL, you can download the Timeshift installer and execute it in your terminal.
$ sudo sh ./timeshift*amd64.run # 64-bit $ sudo sh ./timeshift*i386.run # 32-bitRunning Timeshift for the first time will launch a setup wizard and on completion, you will be ready to start creating snapshots.
I advise that you reconfigure the app after completing the setup wizard steps so you will be able to select user directories that you want to include or use filters to specify files that you want the backup process to include or ignore.
You can always change your settings to fit a different backup scheme from the settings tab.
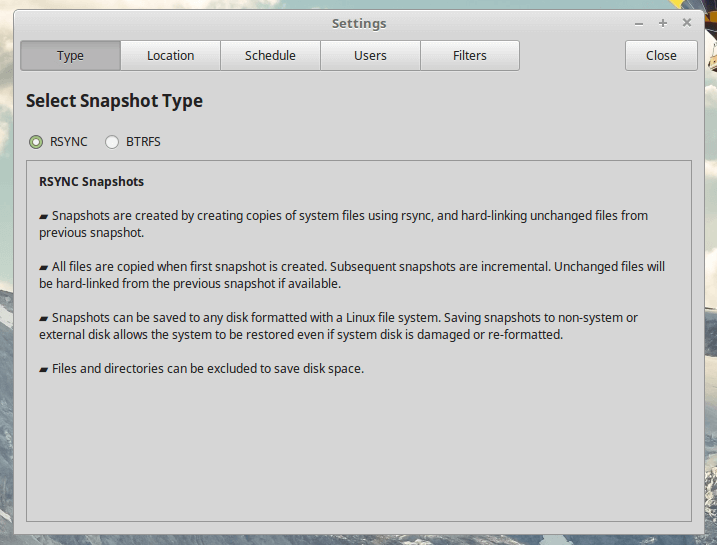
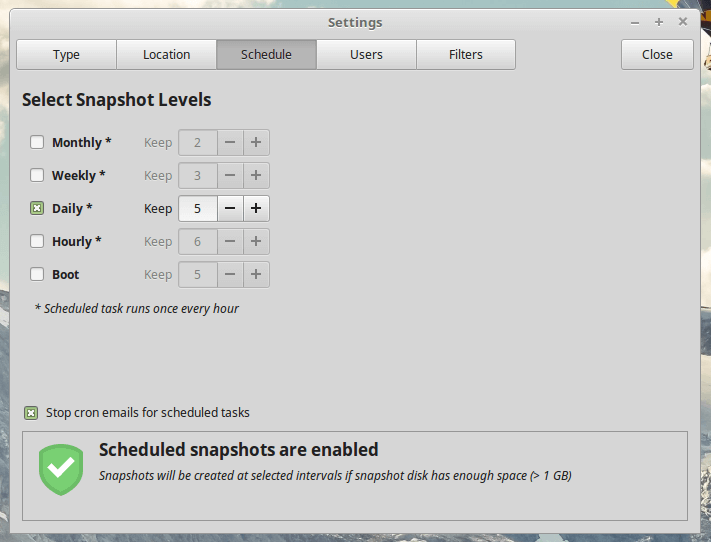
Within the Settings tab are 5 other tabbed sections: Type, Location, Schedule, Users and Filters.
- Type – select to create snapshots using RSYNC or BTRFS mode.
- Location – select the memory location to which snapshots will be saved.
- Schedule – select how often you want to create snapshots and how many of each category to keep.
- Users – where you can enable user home directory backups since they are disabled by default.
- Filters – where you can select files and directories to exclude from snapshots.
Creating & Restoring Backups Using Timeshift
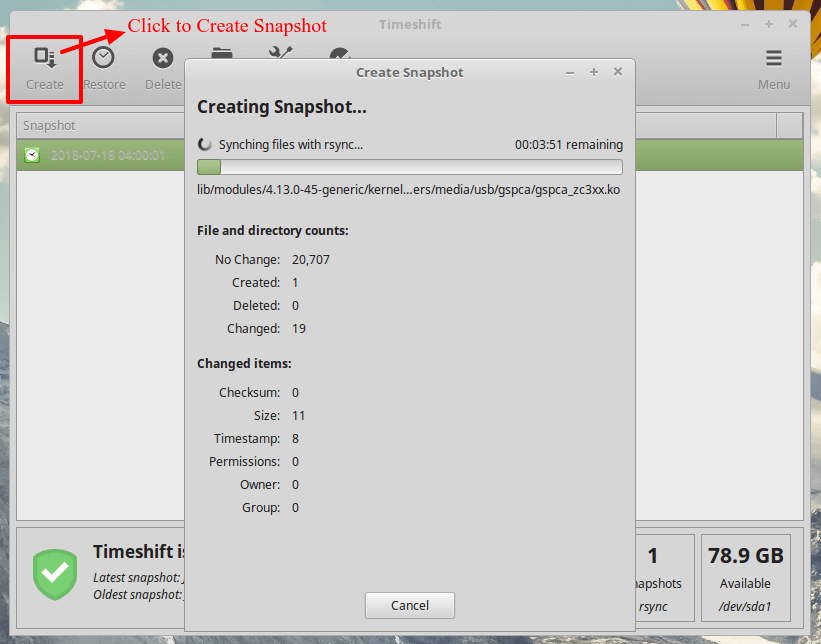
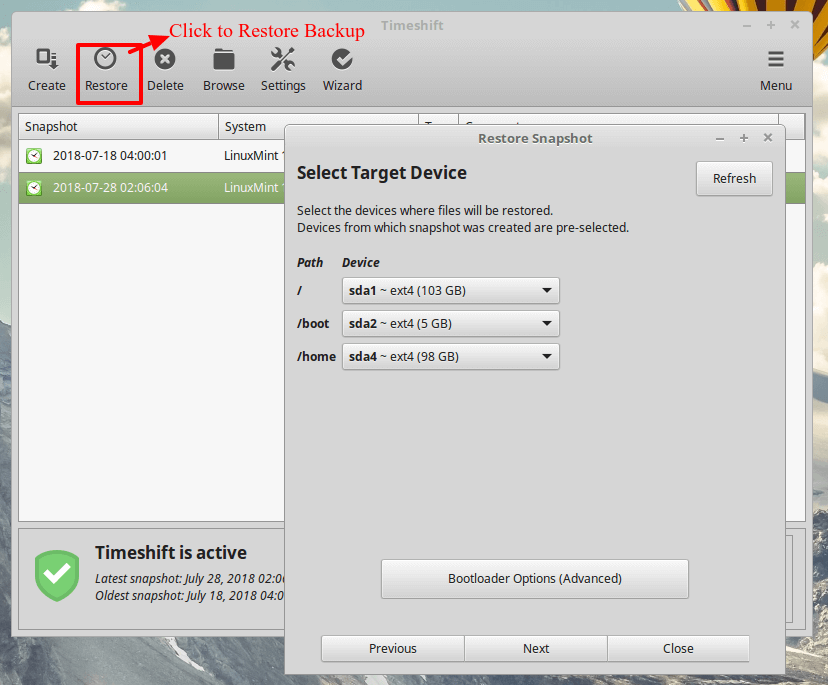
Creating backups is as simple as clicking on the Create button and Timeshift will create a system snapshot using your configured settings.All snapshots will be listed in Timeshift’s main screen. Highlight anyone on the list and click the Restore button to revert to a previous time as saved in the snapshot.
Remember that using Timeshift, requires you to have a sufficient amount of memory to hold at least 1 snapshot. You can reduce the number of backup levels to as little as 1 by unchecking the backup levels to keep only one selected.
You can reduce the snapshots count in the Schedule tab and set the snapshot number to 5 or less. You can also disable automatic backups and create snapshots manually whenever you need one done.
As you can see, Timeshift is easy to use thanks to its helpful descriptions and hints.
How much of a Timeshift user are you? Do you use it to also backup your documents and media files or do you use it for only system snapshots and use a different backup tool for your files?
Drop your comments in the discussion section below.

No comments:
Post a Comment