https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/csf-firewall
CSF stands for Configserver security and firewall. CSF is a configuration script built to provide better security to servers , at the same time providing a large number of configuration options and features to configure and secure with extra checks to ensure smooth operation. It helps in locking down public access and to restrict what can be accessed like only e-mails or only websites, etc. To add more power to this, it comes with a Login Failure Daemon (LFD) script that runs all the time to scan for failed attempts to login to the server to detect bruteforce-attacks. There are an array of extensive checks that lfd can perform to help alert the server administrator of changes to the server, potential problems and possible compromises.
Now we are ready to install, but before we can, we will need to have root privileges else we will not be able to install. So, use the following command to gain root privilege and type in the password if asked.
Once the installation is complete, we can do the verification.To do so, we test if our system has all the required iptables modules. Now when this is run, it might indicate that you might not be able to run all the features but that is alright. This test can be considered as PASS as long as the script doesn't report any FATAL errors. To test it, use the following command:
CSF is installed in the "/etc/csf" directory and the user requires root privileges even to access the directory. This directory consists of all the files required to configure and run the csf. Firstly, "csf.conf" is the file that helps enabling/disabling and managing every possible use and feature of csf. It handles all the configurations. The directory also contains various files like "csf.syslog" that contains where the log files will be kept, "csf.allow" file that is used to allow IP address through the firewall, and many more.
The steps to watch are:
nano /etc/csf/csf.allow
add the following lines ( if the IP you want is different, change it.)
CSF stands for Configserver security and firewall. CSF is a configuration script built to provide better security to servers , at the same time providing a large number of configuration options and features to configure and secure with extra checks to ensure smooth operation. It helps in locking down public access and to restrict what can be accessed like only e-mails or only websites, etc. To add more power to this, it comes with a Login Failure Daemon (LFD) script that runs all the time to scan for failed attempts to login to the server to detect bruteforce-attacks. There are an array of extensive checks that lfd can perform to help alert the server administrator of changes to the server, potential problems and possible compromises.
LFD also blocks IPs if a huge number of failed logins are appearing
from that IP. The block is temporary. It also allows the admin to view
the blocked IP by enabling an email alert service. Some of the features
include:
- Login Tracking
- Process Tracking
- Directory Watching
- Advanced Allow/Deny features
- Block Reporting
- Port Flood Protection
2 Downloading and Installing
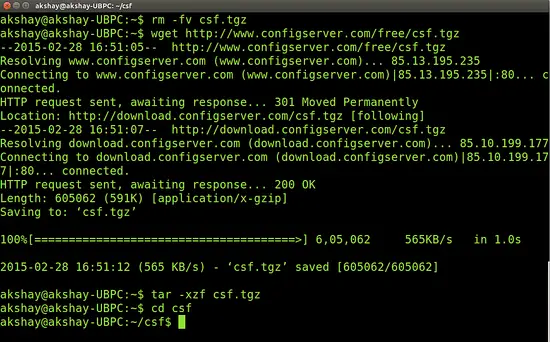
The first step involves removing any previous version of csf that might have been downloaded and then downloading the latest version. To perform these use the following two commands:
rm -fv csf.tgz
wget http://www.configserver.com/free/csf.tgz
Now we extract the tar file in the home directory and move into the csf directory.wget http://www.configserver.com/free/csf.tgz
tar -xzf csf.tgz
cd csf
The steps till here are shown in the image below.cd csf

Now we are ready to install, but before we can, we will need to have root privileges else we will not be able to install. So, use the following command to gain root privilege and type in the password if asked.
sudo su
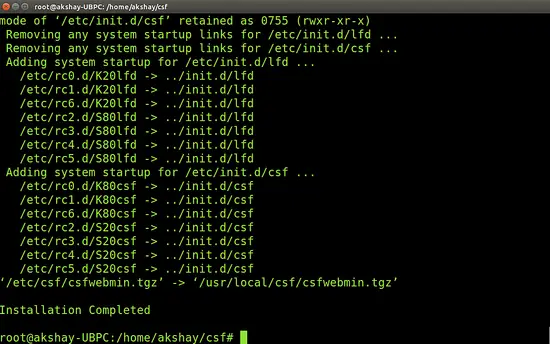
Install CSF using the following command:
sh install.sh
Once the installation is over successfully, the output will look similar to the image below.
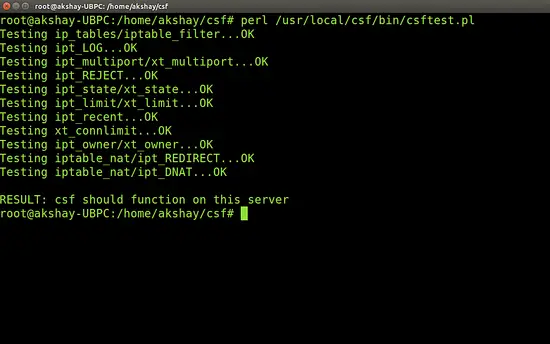
Once the installation is complete, we can do the verification.To do so, we test if our system has all the required iptables modules. Now when this is run, it might indicate that you might not be able to run all the features but that is alright. This test can be considered as PASS as long as the script doesn't report any FATAL errors. To test it, use the following command:
perl /usr/local/csf/bin/csftest.pl
My result of running this test is shown in the image below:
3 Remove other firewalls
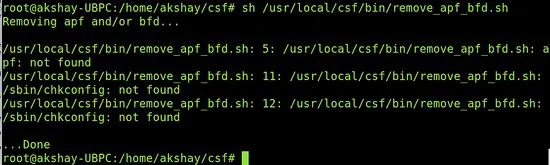
It is important to remove older firewalls or any other firewalls setup to protect the server. This is because the conflict of Firewalls can lead to failures or inaccessibility. You should also not install any other iptables firewall and if it already exists, then it has to be removed at this stage. Most of the systems is likely to have APF+BFD firewalls and has to be removed. So use the following command to detect and remove them if they exist.
sh /usr/local/csf/bin/remove_apf_bfd.sh
I didn't have it pre-installed , so the output of the command in my system looked like the image below:
4 Uninstalling CSF and LFD
If you want to remove CSF completely, then just use the following two commands.
cd /etc/csf
sh uninstall.sh
sh uninstall.sh
5 The configuration
CSF is automatically preconfigured for cPanel and DirectAdmin and will work with all the standard ports open. CSF also csf auto-configures your SSH port on installation where it's running on a non-standard port. CSF also auto-whitelists your connected IP address where possible on installation. But however full control can be taken by the admin and csf can be manually configured to suit the needs of the type of server.CSF is installed in the "/etc/csf" directory and the user requires root privileges even to access the directory. This directory consists of all the files required to configure and run the csf. Firstly, "csf.conf" is the file that helps enabling/disabling and managing every possible use and feature of csf. It handles all the configurations. The directory also contains various files like "csf.syslog" that contains where the log files will be kept, "csf.allow" file that is used to allow IP address through the firewall, and many more.
6 Using CSF to watch IP addresses
the "-w" or the "--watch" option can be used to watch and log packets from a specified source as they traverse the iptables chains. This feature becomes extremely useful when in tracking where that IP address is being dropped or accepted by iptables. Do note that at any time time, only a few IP addresses should be watched and for a short period of time, else the log file gets flooded with these entries. To end the watch you will have to restart csf, as watches do not survive restarts.The steps to watch are:
- Go to the config file present in /etc/csf called "csf.conf" this is the config file. Search for "WATCH_MODE" and make the value "1". This enables it.
- restart the csf and lfd
- use the following command to watch the ip. Make sure you change the IP shown below to what you want.
csf -w 11.22.33.44
- Watch the kernel iptables log for hits from the watched IP address
Firewall: I:INPUT SRC=192.168.254.4 DST=192.168.254.71 PROTO=TCP DPT=22 Firewall: I:LOCALINPUT SRC=192.168.254.4 DST=192.168.254.71 PROTO=TCP DPT=22 Firewall: I:GDENYIN SRC=192.168.254.4 DST=192.168.254.71 PROTO=TCP DPT=22 Firewall: O:GDENYIN SRC=192.168.254.4 DST=192.168.254.71 PROTO=TCP DPT=22 Firewall: I:DSHIELD SRC=192.168.254.4 DST=192.168.254.71 PROTO=TCP DPT=22 Firewall: O:DSHIELD SRC=192.168.254.4 DST=192.168.254.71 PROTO=TCP DPT=22 Firewall: I:SPAMHAUS SRC=192.168.254.4 DST=192.168.254.71 PROTO=TCP DPT=22 Firewall: O:SPAMHAUS SRC=192.168.254.4 DST=192.168.254.71 PROTO=TCP DPT=22 Firewall: O:LOCALINPUT SRC=192.168.254.4 DST=192.168.254.71 PROTO=TCP DPT=22 Firewall: I:INVALID SRC=192.168.254.4 DST=192.168.254.71 PROTO=TCP DPT=22 Firewall: O:INVALID SRC=192.168.254.4 DST=192.168.254.71 PROTO=TCP DPT=22 Firewall: I:LOGACCEPT SRC=192.168.254.4 DST=192.168.254.71 PROTO=TCP DPT=22
7 Allowing Allow/deny filters on IP addresses
csf can be used to add advanced allow and deny filters using the following
tcp/udp|in/out|s/d=port|s/d=ip|u=uid
The break down of this format is shown below:tcp/udp : EITHER tcp OR udp OR icmp protocol
in/out : EITHER incoming OR outgoing connections
s/d=port : EITHER source OR destination port number (or ICMP type)
(use a _ for a port range, e.g. 2000_3000)
s/d=ip : EITHER source OR destination IP address
u/g=UID : EITHER UID or GID of source packet, implies outgoing
connections, s/d=IP value is ignored
7.1 Allowing IP addresses
IP addresses can be excluded individually or in ranges by adding them in the csf.allow file. here lets assume that we want to add the range 2.3.*.*, we represent this is CIDR notation and also we want to allow the IP 192.168.3.215 . to do so, use the following command:nano /etc/csf/csf.allow
add the following lines ( if the IP you want is different, change it.)
2.3.0.0/16 192.168.3.215

No comments:
Post a Comment