https://linuxhint.com/30_bash_script_examples

Bash scripts can be used for various purposes, such as executing a shell
command, running multiple commands together, customizing administrative
tasks, performing task automation etc. So knowledge of bash programming
basics is important for every Linux user. This article will help you to
get the basic idea on bash programming. Most of the common operations
of bash scripting are explained with very simple examples here.
The following topics of bash programming are covered in this article.

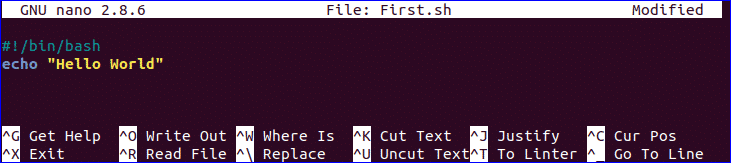
Open any editor to create a bash file. Here, nano editor is used to create the file and filename is set as ‘First.sh’
Add the following bash script to the file and save the file.
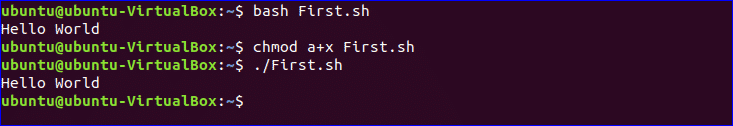
You can run bash file by two ways. One way is by using bash command and another is by setting execute permission to bash file and run the file. Both ways are shown here.
Or,
Go to top
Run the file with bash command.
Go to top
Run the file with bash command.

Go to top
Run the file with bash command.
You can check the following link to know more about the use of bash comment.
https://linuxhint.com/bash_comments/
Go to top
Run the file with bash command.
You can check the following link to know more about the use of while loop.
https://linuxhint.com/bash-while-loop-examples/
Go to top
Run the file with bash command.

You can use for loop for different purposes and ways in your bash script. You can check the following link to know more about the use of for loop.
https://linuxhint.com/bash-for-loop-examples/
Go to top
Run the file with bash command.
You can check the following link to know more about the use of user input.
https://linuxhint.com/bash-script-user-input/
Go to top
Run the file with bash command.

Go to top
Run the file with bash command.
Go to top
Run the file with bash command.
Go to top
Run the file with bash command.
Go to top
Run the file with bash command.
Go to top
Run the file with bash command.
You can check the following link to know more about the use of command line argument.
https://linuxhint.com/command_line_arguments_bash_script/
Go to top
Run the file with bash command and with two command line arguments.

Go to top
Run the file with bash command.
Go to top
Run the file with bash command.

Go to top
Run the file with bash command.
You can check the following link to know more about bash arithmetic.
https://linuxhint.com/bash_arithmetic_operations/
Go to top
Run the file with bash command.

Go to top
Run the file with bash command.

Go to top
Run the file with bash command.
You can check the following link to know more about the use of bash function.
https://linuxhint.com/return-string-bash-functions/
Go to top
Run the file with bash command.
Go to top
Run the file with bash command.
You can check the following link to know more about directory creation.
https://linuxhint.com/bash_mkdir_not_existent_path/
Go to top
Run the file with bash command.
Run the following command to check the original content of ‘book.txt’ file.
You can check the following link to know the different ways to read file.
https://linuxhint.com/read_file_line_by_line_bash/
Go to top
Run the file with bash command.
Go to top
Run the file with bash command.
Go to top
Run the following commands to check the existence of the file. Here, book.txt file exists and book2.txt is not exist in the current location.
Go to top
Run the file with bash command.

Go to top
Run the file with bash command.
Go to top
Run the file with bash command.

You can check the following link to know more about wait command.
Go to top
Run the file with bash command.
You can check the following link to know more about sleep command.
https://linuxhint.com/sleep_command_linux/
Go to top
Hope, after reading this article you have got a basic concept on bash scripting language and you will be able to apply them based on your requirements.
- Hello World
- Echo Command
- Comments
- Multi-line comment
- While Loop
- For Loop
- Get User Input
- If statement
- And Condition if statement
- Or Condition if statement
- Else if and else condition
- Case Condition
- Get Arguments from Command Line
- Get arguments from command line with names
- Combine two strings in a variable
- Get Substring of Strings
- Add 2 numbers into a variable
- Create a Function
- Use Function Parameters
- Pass Return Value from Script
- Make directory
- Make directory by checking existence
- Read a file
- Delete a File
- Append to file
- Test if File Exists
- Send Email Example
- Get Parse Current Date
- Wait Command
- Sleep Command
Create and Execute First BASH Program:
You can run bash script from the terminal or by executing any bash file. Run the following command from the terminal to execute a very simple bash statement. The output of the command will be ‘Hello World’.
$ echo "Hello World"

Open any editor to create a bash file. Here, nano editor is used to create the file and filename is set as ‘First.sh’
$ nano First.sh
#!/bin/bash
echo "Hello World"
echo "Hello World"

You can run bash file by two ways. One way is by using bash command and another is by setting execute permission to bash file and run the file. Both ways are shown here.
$ bash First.sh
$ chmod a+x First.sh
$ ./First.sh
$ ./First.sh

Go to top
Use of echo command:
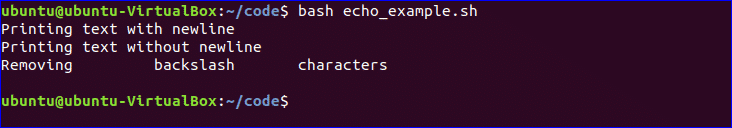
You can use echo command with various options. Some useful options are mentioned in the following example. When you use ‘echo’ command without any option then a newline is added by default. ‘-n’ option is used to print any text without new line and ‘-e’ option is used to remove backslash characters from the output. Create a new bash file with a name, ‘echo_example.sh’ and add the following script.
#!/bin/bash
echo "Printing text with newline"
echo -n "Printing text without newline"
echo -e "\nRemoving \t backslash \t characters\n"
echo "Printing text with newline"
echo -n "Printing text without newline"
echo -e "\nRemoving \t backslash \t characters\n"
$ bash echo_example.sh

Go to top
Use of comment:
‘#’ symbol is used to add single line comment in bash script. Create a new file named ‘comment_example.sh’ and add the following script with single line comment.
#!/bin/bash
# Add two numeric value
((sum=25+35))
#Print the result
echo $sum
# Add two numeric value
((sum=25+35))
#Print the result
echo $sum
$ bash comment_example.sh

Go to top
Use of Multi-line comment:
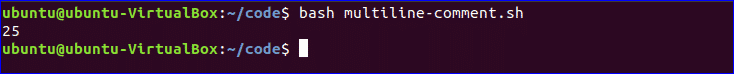
You can use multi line comment in bash in various ways. A simple way is shown in the following example. Create a new bash named, ‘multiline-comment.sh’ and add the following script. Here, ‘:’ and “ ’ ” symbols are used to add multiline comment in bash script. This following script will calculate the square of 5.
#!/bin/bash
: '
The following script calculates
the square value of the number, 5.
'
((area=5*5))
echo $area
: '
The following script calculates
the square value of the number, 5.
'
((area=5*5))
echo $area
$ bash multiline-comment.sh

You can check the following link to know more about the use of bash comment.
https://linuxhint.com/bash_comments/
Go to top
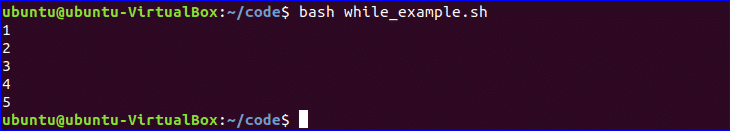
Using While Loop:
Create a bash file with the name, ‘while_example.sh’, to know the use of while loop. In the example, while loop will iterate for 5 times. The value of count variable will increment by 1 in each step. When the value of count variable will 5 then the while loop will terminate.
#!/bin/bash
valid=true
count=1
while [ $valid ]
do
echo $count
if [ $count -eq 5 ];
then
break
fi
((count++))
done
valid=true
count=1
while [ $valid ]
do
echo $count
if [ $count -eq 5 ];
then
break
fi
((count++))
done
$ bash while_example.sh

You can check the following link to know more about the use of while loop.
https://linuxhint.com/bash-while-loop-examples/
Go to top
Using For Loop:
The basic for loop declaration is shown in the following example. Create a file named ‘for_example.sh’ and add the following script using for loop. Here, for loop will iterate for 10 times and print all values of the variable, counter in single line.
#!/bin/bash
for (( counter=10; counter>0; counter-- ))
do
echo -n "$counter "
done
printf "\n"
for (( counter=10; counter>0; counter-- ))
do
echo -n "$counter "
done
printf "\n"
$ bash for_example.sh

You can use for loop for different purposes and ways in your bash script. You can check the following link to know more about the use of for loop.
https://linuxhint.com/bash-for-loop-examples/
Go to top
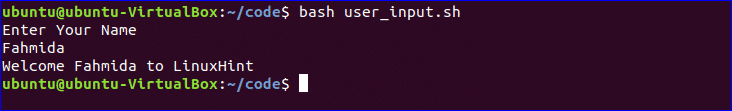
Get User Input:
‘read’ command is used to take input from user in bash. Create a file named ‘user_input.sh’ and add the following script for taking input from the user. Here, one string value will be taken from the user and display the value by combining other string value.
#!/bin/bash
echo "Enter Your Name"
read name
echo "Welcome $name to LinuxHint"
echo "Enter Your Name"
read name
echo "Welcome $name to LinuxHint"
$ bash user_input.sh

You can check the following link to know more about the use of user input.
https://linuxhint.com/bash-script-user-input/
Go to top
Using if statement:
You can use if condition with single or multiple conditions. Starting and ending block of this statement is define by ‘if’ and ‘fi’. Create a file named ‘simple_if.sh’ with the following script to know the use if statement in bash. Here, 10 is assigned to the variable, n. if the value of $n is less than 10 then the output will be “It is a one digit number”, otherwise the output will be “It is a two digit number”. For comparison, ‘-lt’ is used here. For comparison, you can also use ‘-eq’ for equality, ‘-ne’ for not equality and ‘-gt’ for greater than in bash script.
#!/bin/bash
n=10
if [ $n -lt 10 ];
then
echo "It is a one digit number"
else
echo "It is a two digit number"
fi
n=10
if [ $n -lt 10 ];
then
echo "It is a one digit number"
else
echo "It is a two digit number"
fi
$ bash simple_if.sh

Go to top
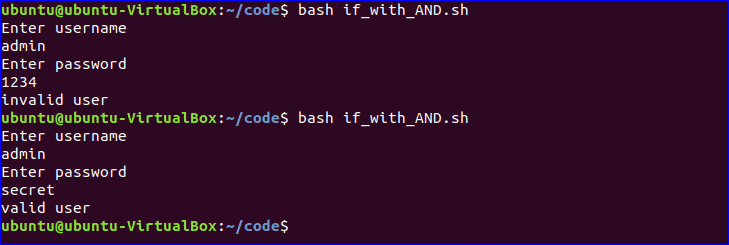
Using if statement with AND logic:
Different types of logical conditions can be used in if statement with two or more conditions. How you can define multiple conditions in if statement using AND logic is shown in the following example. ‘&&’ is used to apply AND logic of if statement. Create a file named ‘if_with_AND.sh’ to check the following code. Here, the value of username and password variables will be taken from the user and compared with ‘admin’ and ‘secret’. If both values match then the output will be “valid user”, otherwise the output will be “invalid user”.
!/bin/bash
echo "Enter username"
read username
echo "Enter password"
read password
if [[ ( $username == "admin" && $password == "secret" ) ]]; then
echo "valid user"
else
echo "invalid user"
fi
echo "Enter username"
read username
echo "Enter password"
read password
if [[ ( $username == "admin" && $password == "secret" ) ]]; then
echo "valid user"
else
echo "invalid user"
fi
$ bash if_with_AND.sh

Go to top
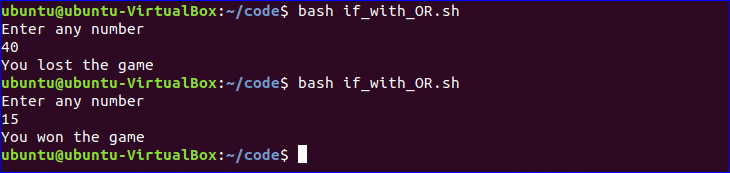
Using if statement with OR logic:
‘||’ is used to define OR logic in if condition. Create a file named ‘if_with_OR.sh’ with the following code to check the use of OR logic of if statement. Here, the value of n will be taken from the user. If the value is equal to 15 or 45 then the output will be “You won the game”, otherwise the output will be “You lost the game”.
#!/bin/bash
echo "Enter any number"
read n
if [[ ( $n -eq 15 || $n -eq 45 ) ]]
then
echo "You won the game"
else
echo "You lost the game"
fi
echo "Enter any number"
read n
if [[ ( $n -eq 15 || $n -eq 45 ) ]]
then
echo "You won the game"
else
echo "You lost the game"
fi
$ bash if_with_OR.sh

Go to top
Using else if statement:
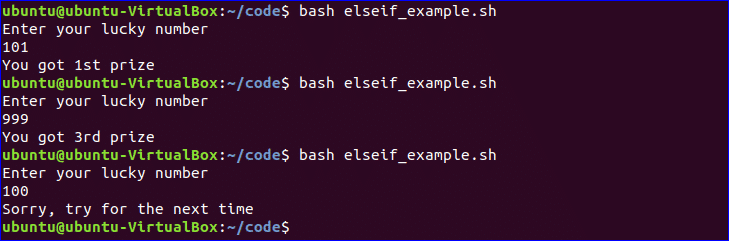
The use of else if condition is little different in bash than other programming language. ‘elif’ is used to define else if condition in bash. Create a file named, ‘elseif_example.sh’ and add the following script to check how else if is defined in bash script.
#!/bin/bash
echo "Enter your lucky number"
read n
if [ $n -eq 101 ];
then
echo "You got 1st prize"
elif [ $n -eq 510 ];
then
echo "You got 2nd prize"
elif [ $n -eq 999 ];
then
echo "You got 3rd prize"
else
echo "Sorry, try for the next time"
fi
echo "Enter your lucky number"
read n
if [ $n -eq 101 ];
then
echo "You got 1st prize"
elif [ $n -eq 510 ];
then
echo "You got 2nd prize"
elif [ $n -eq 999 ];
then
echo "You got 3rd prize"
else
echo "Sorry, try for the next time"
fi
$ bash elseif_example.sh

Go to top
Using Case Statement:
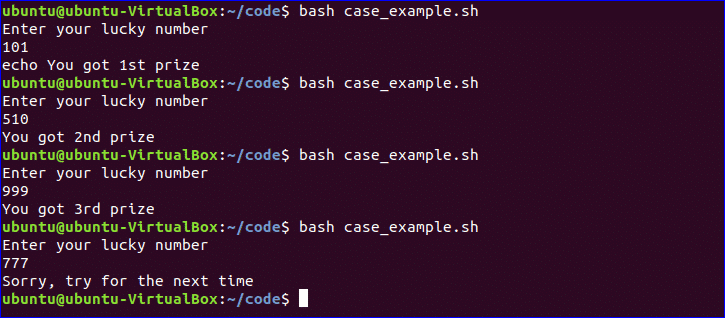
Case statement is used as the alternative of if-elseif-else statement. The starting and ending block of this statement is defined by ‘case’ and ‘esac’. Create a new file named, ‘case_example.sh’ and add the following script. The output of the following script will be same to the previous else if example.
#!/bin/bash
echo "Enter your lucky number"
read n
case $n in
101)
echo echo "You got 1st prize" ;;
510)
echo "You got 2nd prize" ;;
999)
echo "You got 3rd prize" ;;
*)
echo "Sorry, try for the next time" ;;
esac
echo "Enter your lucky number"
read n
case $n in
101)
echo echo "You got 1st prize" ;;
510)
echo "You got 2nd prize" ;;
999)
echo "You got 3rd prize" ;;
*)
echo "Sorry, try for the next time" ;;
esac
$ bash case_example.sh

Go to top
Get Arguments from Command Line:
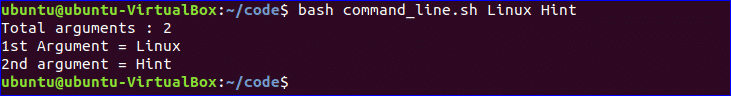
Bash script can read input from command line argument like other programming language. For example, $1 and $2 variable are used to read first and second command line arguments. Create a file named “command_line.sh” and add the following script. Two argument values read by the following script and prints the total number of arguments and the argument values as output.
#!/bin/bash
echo "Total arguments : $#"
echo "1st Argument = $1"
echo "2nd argument = $2"
echo "Total arguments : $#"
echo "1st Argument = $1"
echo "2nd argument = $2"
$ bash command_line.sh Linux Hint

You can check the following link to know more about the use of command line argument.
https://linuxhint.com/command_line_arguments_bash_script/
Go to top
Get arguments from command line with names:
How you can read command line arguments with names is shown in the following script. Create a file named, ‘command_line_names.sh’ and add the following code. Here, two arguments, X and Y are read by this script and print the sum of X and Y.
#!/bin/bash
for arg in "$@"
do
index=$(echo $arg | cut -f1 -d=)
val=$(echo $arg | cut -f2 -d=)
case $index in
X) x=$val;;
Y) y=$val;;
*)
esac
done
((result=x+y))
echo "X+Y=$result"
for arg in "$@"
do
index=$(echo $arg | cut -f1 -d=)
val=$(echo $arg | cut -f2 -d=)
case $index in
X) x=$val;;
Y) y=$val;;
*)
esac
done
((result=x+y))
echo "X+Y=$result"
$ bash command_line_names X=45 Y=30

Go to top
Combine String variables:
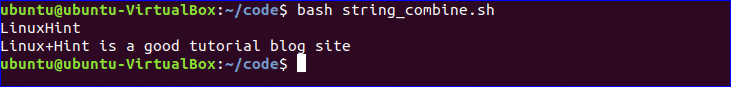
You can easily combine string variables in bash. Create a file named “string_combine.sh” and add the following script to check how you can combine string variables in bash by placing variables together or using ‘+’ operator.
#!/bin/bash
string1="Linux"
string2="Hint"
echo "$string1$string2"
string3=$string1+$string2
string3+=" is a good tutorial blog site"
echo $string3
string1="Linux"
string2="Hint"
echo "$string1$string2"
string3=$string1+$string2
string3+=" is a good tutorial blog site"
echo $string3
$ bash string_combine.sh

Go to top
Get substring of String:
Like other programming language, bash has no built-in function to cut value from any string data. But you can do the task of substring in another way in bash that is shown in the following script. To test the script, create a file named ‘substring_example.sh’ with the following code. Here, the value, 6 indicates the starting point from where the substring will start and 5 indicates the length of the substring.
#!/bin/bash
Str="Learn Linux from LinuxHint"
subStr=${Str:6:5}
echo $subStr
Str="Learn Linux from LinuxHint"
subStr=${Str:6:5}
echo $subStr
$ bash substring_example.sh

Go to top
Add Two Numbers:
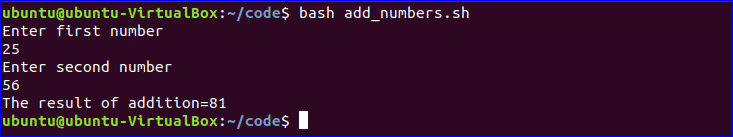
You can do the arithmetical operations in bash in different ways. How you can add two integer numbers in bash using double brackets is shown in the following script. Create a file named ‘add_numbers.sh’ with the following code. Two integer values will be taken from the user and printed the result of addition.
#!/bin/bash
echo "Enter first number"
read x
echo "Enter second number"
read y
(( sum=x+y ))
echo "The result of addition=$sum"
echo "Enter first number"
read x
echo "Enter second number"
read y
(( sum=x+y ))
echo "The result of addition=$sum"
$ bash add_numbers.sh

You can check the following link to know more about bash arithmetic.
https://linuxhint.com/bash_arithmetic_operations/
Go to top
Create Function:
How you can create a simple function and call the function is shown in the following script. Create a file named ‘function_example.sh’ and add the following code. You can call any function by name only without using any bracket in bash script.
#!/bin/bash
function F1()
{
echo 'I like bash programming'
}
F1
function F1()
{
echo 'I like bash programming'
}
F1
$ bash function_example.sh

Go to top
Create function with Parameters:
Bash can’t declare function parameter or arguments at the time of function declaration. But you can use parameters in function by using other variable. If two values are passed at the time of function calling then $1 and $2 variable are used for reading the values. Create a file named ‘function|_parameter.sh’ and add the following code. Here, the function, ‘Rectangle_Area’ will calculate the area of a rectangle based on the parameter values.
#!/bin/bash
Rectangle_Area() {
area=$(($1 * $2))
echo "Area is : $area"
}
Rectangle_Area 10 20
Rectangle_Area() {
area=$(($1 * $2))
echo "Area is : $area"
}
Rectangle_Area 10 20
$ bash function_parameter.sh

Go to top
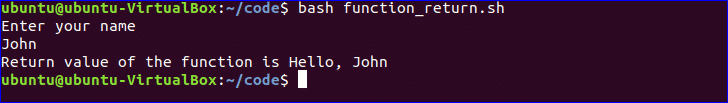
Pass Return Value from Function:
Bash function can pass both numeric and string values. How you can pass a string value from the function is shown in the following example. Create a file named, ‘function_return.sh’ and add the following code. The function, greeting() returns a string value into the variable, val which prints later by combining with other string.
#!/bin/bash
function greeting() {
str="Hello, $name"
echo $str
}
echo "Enter your name"
read name
val=$(greeting)
echo "Return value of the function is $val"
function greeting() {
str="Hello, $name"
echo $str
}
echo "Enter your name"
read name
val=$(greeting)
echo "Return value of the function is $val"
$ bash function_return.sh

You can check the following link to know more about the use of bash function.
https://linuxhint.com/return-string-bash-functions/
Go to top
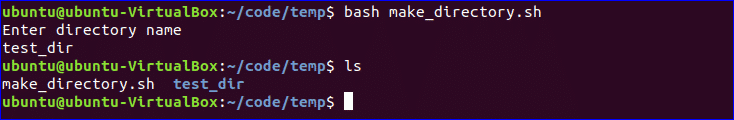
Make Directory:
Bash uses ‘mkdir’ command to create a new directory. Create a file named ‘make_directory.sh’ and add the following code to take a new directory name from the user. If the directory name is not exist in the current location then it will create the directory, otherwise the program will display error.
#!/bin/bash
echo "Enter directory name"
read newdir
`mkdir $newdir`
echo "Enter directory name"
read newdir
`mkdir $newdir`
$ bash make_directory.sh

Go to top
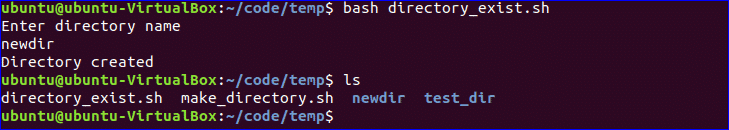
Make directory by checking existence:
If you want to check the existence of directory in the current location before executing the ‘mkdir’ command then you can use the following code. ‘-d’ option is used to test a particular directory is exist or not. Create a file named, ‘directory_exist.sh’ and add the following code to create a directory by checking existence.
#!/bin/bash
echo "Enter directory name"
read ndir
if [ -d "$ndir" ]
then
echo "Directory exist"
else
`mkdir $ndir`
echo "Directory created"
fi
echo "Enter directory name"
read ndir
if [ -d "$ndir" ]
then
echo "Directory exist"
else
`mkdir $ndir`
echo "Directory created"
fi
$ bash directory_exist.sh

You can check the following link to know more about directory creation.
https://linuxhint.com/bash_mkdir_not_existent_path/
Go to top
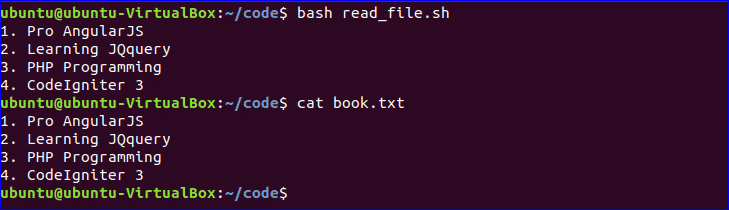
Read a File:
You can read any file line by line in bash by using loop. Create a file named, ‘read_file.sh’ and add the following code to read an existing file named, ‘book.txt’.
#!/bin/bash
file='book.txt'
while read line; do
echo $line
done < $file
file='book.txt'
while read line; do
echo $line
done < $file
$ bash read_file.sh
$ cat book.txt

You can check the following link to know the different ways to read file.
https://linuxhint.com/read_file_line_by_line_bash/
Go to top
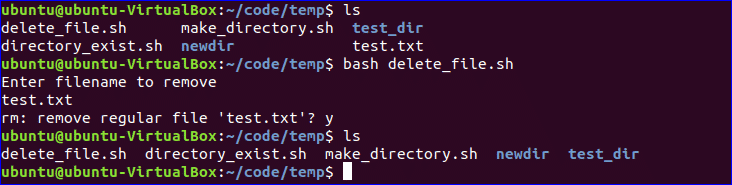
Delete a File:
‘rm’ command is used in bash to remove any file. Create a file named ‘delete_file.sh’ with the following code to take the filename from the user and remove. Here, ‘-i’ option is used to get permission from the user before removing the file.
#!/bin/bash
echo "Enter filename to remove"
read fn
rm -i $fn
echo "Enter filename to remove"
read fn
rm -i $fn
$ ls
$ bash delete_file.sh
$ ls
$ bash delete_file.sh
$ ls

Go to top
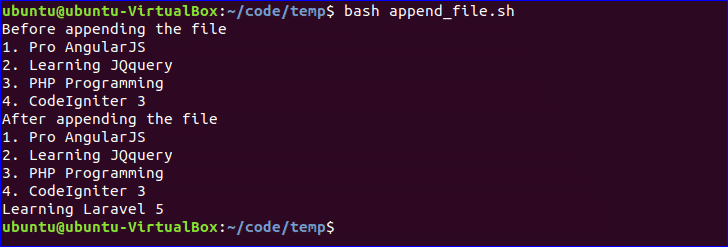
Append to File:
New data can be added into any existing file by using ‘>>’ operator in bash. Create a file named ‘append_file.sh’ and add the following code to add new content at the end of the file. Here, ‘Learning Laravel 5’ will be added at the of ‘book.txt’ file after executing the script.
#!/bin/bash
echo "Before appending the file"
cat book.txt
echo "Learning Laravel 5">> book.txt
echo "After appending the file"
cat book.txt
echo "Before appending the file"
cat book.txt
echo "Learning Laravel 5">> book.txt
echo "After appending the file"
cat book.txt
$ bash append_file.sh

Go to top
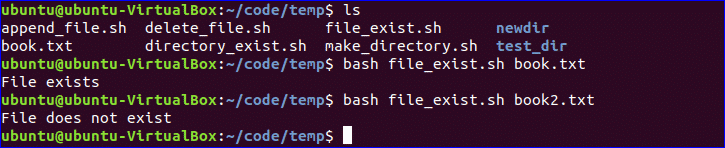
Test if File Exist:
You can check the existence of file in bash by using ‘-e’ or ‘-f’ option. ‘-f’ option is used in the following script to test the file existence. Create a file named, ‘file_exist.sh’ and add the following code. Here, the filename will pass from the command line.
#!/bin/bash
filename=$1
if [ -f "$filename" ]; then
echo "File exists"
else
echo "File does not exist"
fi
filename=$1
if [ -f "$filename" ]; then
echo "File exists"
else
echo "File does not exist"
fi
$ ls
$ bash file_exist.sh book.txt
$ bash file_exist.sh book2.txt
$ bash file_exist.sh book.txt
$ bash file_exist.sh book2.txt

Go to top
Send Email:
You can send email by using ‘mail’ or ‘sendmail’ command. Before using these commands, you have to install all necessary packages. Create a file named, ‘mail_example.sh’ and add the following code to send the email.
#!/bin/bash
Recipient=”admin@example.com”
Subject=”Greeting”
Message=”Welcome to our site”
`mail -s $Subject $Recipient <<< $Message`
Recipient=”admin@example.com”
Subject=”Greeting”
Message=”Welcome to our site”
`mail -s $Subject $Recipient <<< $Message`
$ bash mail_example.sh

Go to top
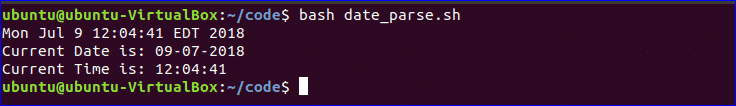
Get Parse Current Date:
You can get the current system date and time value using `date` command. Every part of date and time value can be parsed using ‘Y’, ‘m’, ‘d’, ‘H’, ‘M’ and ‘S’. Create a new file named ‘date_parse.sh’ and add the following code to separate day, month, year, hour, minute and second values.
#!/bin/bash
Year=`date +%Y`
Month=`date +%m`
Day=`date +%d`
Hour=`date +%H`
Minute=`date +%M`
Second=`date +%S`
echo `date`
echo "Current Date is: $Day-$Month-$Year"
echo "Current Time is: $Hour:$Minute:$Second"
Year=`date +%Y`
Month=`date +%m`
Day=`date +%d`
Hour=`date +%H`
Minute=`date +%M`
Second=`date +%S`
echo `date`
echo "Current Date is: $Day-$Month-$Year"
echo "Current Time is: $Hour:$Minute:$Second"
$ bash date_parse.sh

Go to top
Wait Command:
wait is a built-in command of Linux that waits for completing any running process. wait command is used with a particular process id or job id. If no process id or job id is given with wait command then it will wait for all current child processes to complete and returns exit status. Create a file named ‘wait_example.sh’ and add the following script.
#!/bin/bash
echo "Wait command" &
process_id=$!
wait $process_id
echo "Exited with status $?"
echo "Wait command" &
process_id=$!
wait $process_id
echo "Exited with status $?"
$ bash wait_example.sh

You can check the following link to know more about wait command.
Go to top
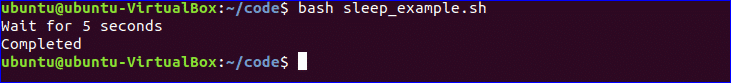
Sleep Command:
When you want to pause the execution of any command for specific period of time then you can use sleep command. You can set the delay amount by seconds (s), minutes (m), hours (h) and days (d). Create a file named ‘sleep_example.sh’ and add the following script. This script will wait for 5 seconds after running.
#!/bin/bash
echo “Wait for 5 seconds”
sleep 5
echo “Completed”
echo “Wait for 5 seconds”
sleep 5
echo “Completed”
$ bash sleep_example.sh

You can check the following link to know more about sleep command.
https://linuxhint.com/sleep_command_linux/
Go to top
Hope, after reading this article you have got a basic concept on bash scripting language and you will be able to apply them based on your requirements.
About the author
Fahmida Yesmin
I am a trainer of web programming courses. I like to write article or
tutorial on various IT topics. I have a YouTube channel where many
types of tutorials based on Ubuntu, Windows, Word, Excel, WordPress,
Magento, Laravel etc. are published: Tutorials4u Help.

No comments:
Post a Comment