https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/how-to-install-and-run-android-apk-on-linux-with-shashlik
Shashlik is basically a set of software components that allow Linux users to install and run Android APKs right on their GNU/Linux distribution. Shashlik achieves that by using a stripped down version of Android instead of emulating one, which is nested inside the user session upon the launching of an installed Android application. The rendering of the graphics in the app is undertaken by the OpenGL infrastructure of our system, so the performance is good for what is well supported.
Unfortunately, Shashlik is still under heavy development and doesn't
support many applications yet, but still you may find many useful apps
that are working like a charm.
The only absolute prerequisites are that you are not running another
virtualization process in the same time that you are trying to run
Shashlik, that the APK used in Shashlik was built to run on x86
architecture, and that Shashlik is installed on a 64-bit Linux system.
Its developers also suggest running their software on the KDE Plasma
environment, as they are testing it on this only, but I can also confirm
that it works on Pantheon as well (with some relevant error messages).
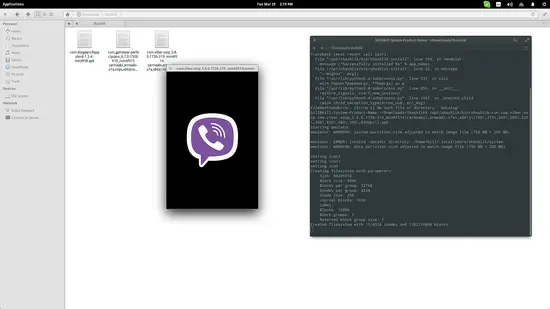
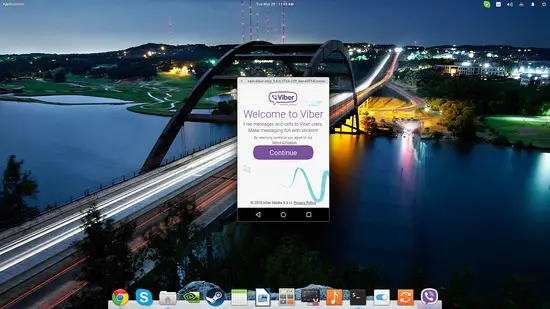
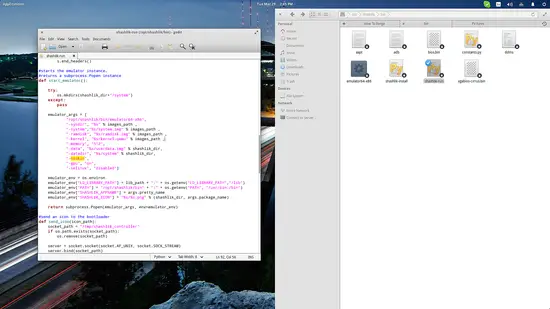
Next step is to run the APK by typing the following command on the same terminal session: “/opt/shashlik/bin/shashlik-run name_of_splash_png name_of_apk_file”. One important thing to note at this point is that during the installation, Shashlik has created and stored some required files in /.local/share/shashlik. Those files include the splash png image file and the userdata.img. Upon launching an APK, Shashlik looks for the file you have indicated in the command. So, if there is a splash.png corresponding to an application named test.apk, the command becomes: “/opt/shashlik/bin/shashlik-run splash test.apk”. Here's how I did it for Viber
To make things simpler, I should point out that the APKs are
installed in our system with the command I showed previously, so if you
look for them in the applications menu/dash you should find them and run
them with a simple click. This however, may not work well for all apps,
but if it does it's quite handy. Whatever the case, you should know how
to run it from the terminal in order to get the insight needed to solve
any issues.
As there is currently no uninstall function implemented, you can manually remove the binaries installed by Shashlik by navigating to /.local/share/applications and deleting the corresponding files. This should remove them from your applications menu.
Shashlik is basically a set of software components that allow Linux users to install and run Android APKs right on their GNU/Linux distribution. Shashlik achieves that by using a stripped down version of Android instead of emulating one, which is nested inside the user session upon the launching of an installed Android application. The rendering of the graphics in the app is undertaken by the OpenGL infrastructure of our system, so the performance is good for what is well supported.
Installing Shashlik
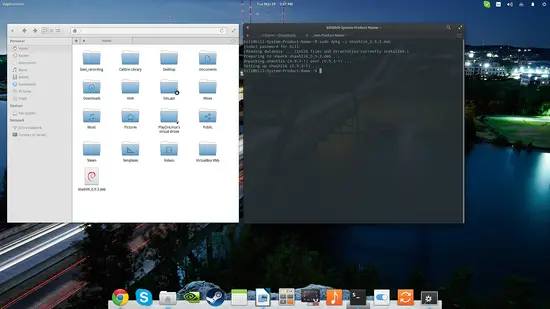
Shashik's latest version at the time of writing this is 0.9.3 which you can download from this web page. There are Debian (Ubuntu) and Arch pre-built packages that you may use depending on your system, while several users of Fedora and Suse systems report that alien-generated RPMs work as well. Ubuntu users may install the downloaded package by opening a terminal on the download location and typing the following command:
sudo dpkg -i shashlik_0.9.3.deb
You may also try to compile Shashlik from source by following the instructions found on the official website,
but I wouldn't recommend this option as you will have to move the
binaries and libraries in the right locations yourself – at least for
now.Installing and Running Android APKs
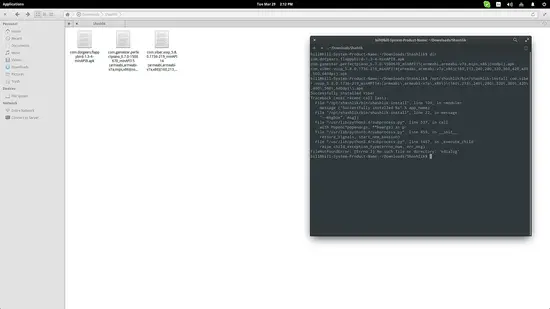
After Shashlik is installed, visit an APK database and download the application that you want to run with Shashlik. Then open a terminal on the location of the downloaded APKs and type the following command to install it to your system: “/opt/shashlik/bin/shashlik-install name_of_apk_file”. As an example, I installed the Viber apk as shown in the following screenshot:Next step is to run the APK by typing the following command on the same terminal session: “/opt/shashlik/bin/shashlik-run name_of_splash_png name_of_apk_file”. One important thing to note at this point is that during the installation, Shashlik has created and stored some required files in /.local/share/shashlik. Those files include the splash png image file and the userdata.img. Upon launching an APK, Shashlik looks for the file you have indicated in the command. So, if there is a splash.png corresponding to an application named test.apk, the command becomes: “/opt/shashlik/bin/shashlik-run splash test.apk”. Here's how I did it for Viber
As there is currently no uninstall function implemented, you can manually remove the binaries installed by Shashlik by navigating to /.local/share/applications and deleting the corresponding files. This should remove them from your applications menu.

No comments:
Post a Comment